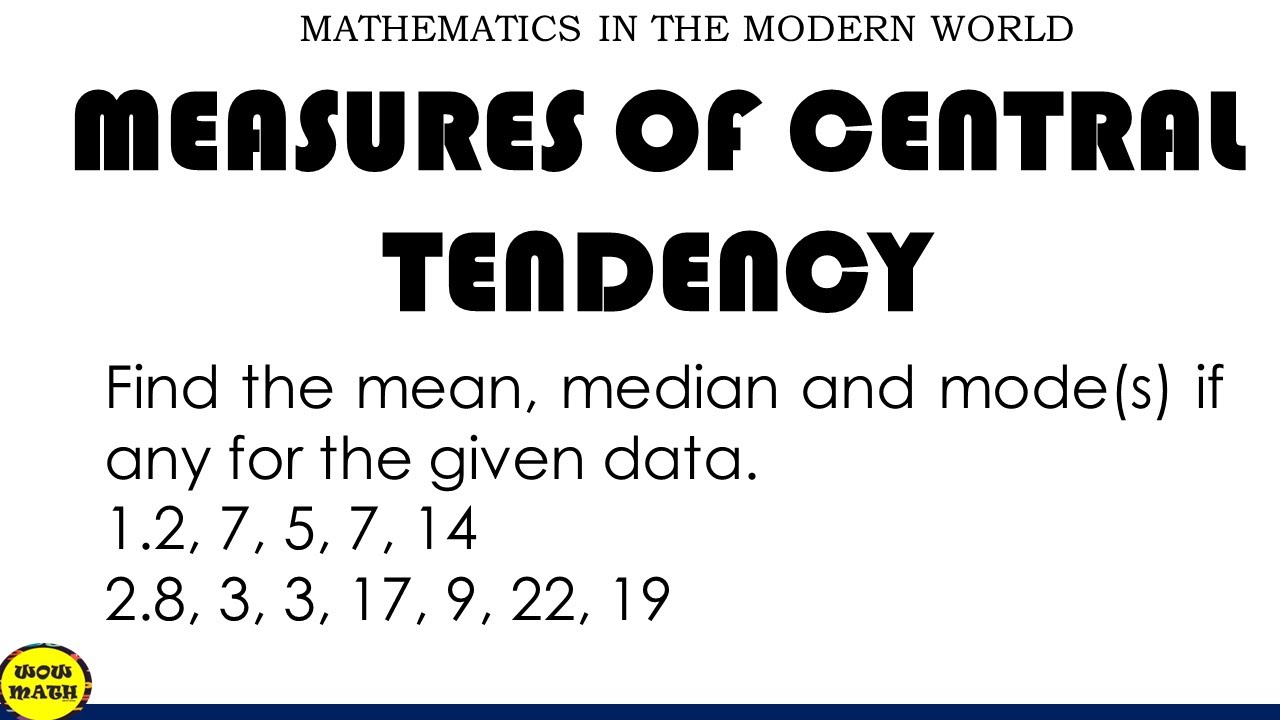
Brief Summary
This video explains how to calculate the mean, median, and mode for a given set of data. The video demonstrates these concepts with two examples, providing step-by-step instructions and explanations.
- The mean is calculated by summing all the values in the data set and dividing by the total number of values.
- The median is the middle value in a sorted data set. If there are an even number of values, the median is the average of the two middle values.
- The mode is the value that appears most frequently in the data set.
Mean, Median, and Mode: Example 1
The first example uses the data set: 2, 7, 5, 7, and 14.
- To find the mean, the values are added together (2 + 7 + 5 + 7 + 14 = 35) and then divided by the number of values (35 / 5 = 7). Therefore, the mean is 7.
- To find the median, the data set is arranged in ascending order (2, 5, 7, 7, 14). Since there are an odd number of values, the middle value (7) is the median.
- To find the mode, the data set is examined for the most frequent value. In this case, the value 7 appears twice, making it the mode. This data set is considered unimodal because it has only one mode.
Mean, Median, and Mode: Example 2
The second example uses the data set: 8, 3, 3, 17, 9, 22, and 19.
- To find the mean, the values are added together (8 + 3 + 3 + 17 + 9 + 22 + 19 = 81) and then divided by the number of values (81 / 7 = 11.57). Therefore, the mean is 11.57.
- To find the median, the data set is arranged in ascending order (3, 3, 8, 9, 17, 19, 22). Since there are an odd number of values, the middle value (9) is the median.
- To find the mode, the data set is examined for the most frequent value. In this case, the value 3 appears twice, making it the mode. This data set is also considered unimodal because it has only one mode.