Brief Summary
This video explains how mutations, which are changes in the genetic code, can lead to evolution through natural selection. Most mutations have no effect, some are harmful, but some can provide an advantage. Only mutations in gametes (sex cells) can be passed on to offspring and influence the gene pool, potentially leading to evolution if the mutation is beneficial and increases in frequency over generations.
- Mutations are changes in the genetic code and the ultimate source of variation.
- Mutations in body cells cannot be passed to offspring and do not influence evolution.
- Only mutations in gametes can be inherited and potentially drive evolution through natural selection.
Introduction to Mutations
Mutations are changes in the genetic code, often resulting from copying errors during DNA replication. While many mutations have no noticeable effect on an organism, some can alter important genes. These alterations can be harmful, decreasing the organism's chances of survival, or beneficial, providing a new trait that gives the organism an advantage. Mutations are the fundamental source of the variety of genes and traits observed in life on Earth.
Mutations That Cannot Lead to Evolution
Mutations that occur in body cells during an organism's lifetime cannot lead to evolution. These mutations are only passed on through mitosis to new body cells and are not inherited by offspring. Even if a body cell mutation is beneficial to the individual, it will not influence the gene pool or affect the traits of future generations.
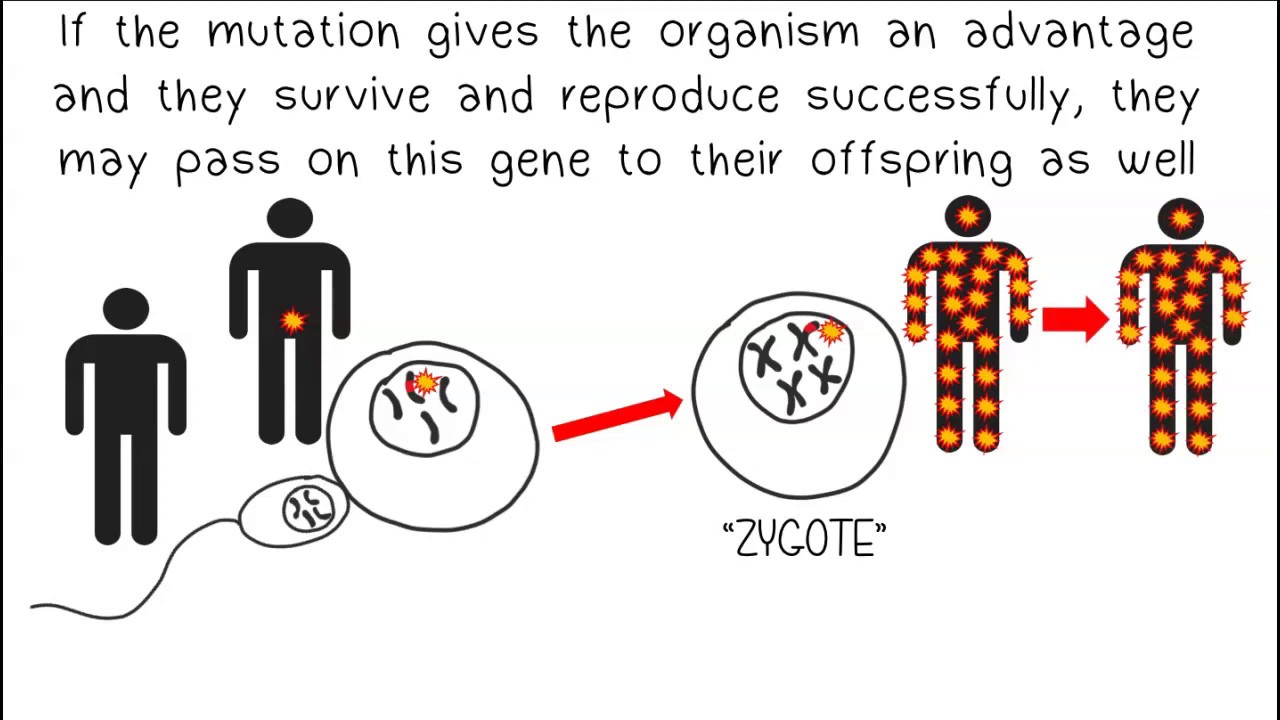
Mutations That Can Lead to Evolution
For a mutation to influence the gene pool and potentially lead to evolution, it must be present in the gametes (sex cells). Gametes unite during sexual reproduction to pass on genetic material from parents to offspring. Mutations in gametes are inherited by the offspring's first cell (zygote) through fertilization, making the mutation present in all cells of the offspring. If the mutation provides an advantage, the organism is more likely to survive and reproduce, passing the gene on to its offspring. Beneficial mutations, through natural selection, may increase in frequency from one generation to the next, leading to evolution, which is the change of a gene pool over time, affecting the traits and survival of individuals in a population.