Brief Summary
This video explains how AI works, learns, and generates content, addressing concerns about AI copying or stealing art and its potential to solve complex problems. It also explores whether AI can surpass human capabilities and if it possesses consciousness or self-awareness. The core of AI lies in neural networks, which mimic the human brain's structure, and deep learning, which involves training these networks with vast amounts of data.
- Neural networks are the backbone of AI, consisting of interconnected nodes and layers that process data.
- AI learns through supervised and unsupervised learning, adjusting its parameters based on feedback and algorithms like gradient descent.
- Image generation involves training AI on images with text descriptions, using processes like forward and reverse diffusion to create new images.
- The debate around AI copying or stealing art is compared to human learning and fan art creation, questioning the validity of plagiarism claims.
- AI's ability to solve complex problems hinges on its capacity to approximate patterns, even without understanding the underlying formulas.
- The question of AI consciousness is explored through analogies to the human brain and discussions on whether AI can possess subjective experiences.
Intro
The video addresses questions about how AI functions, learns, and its potential impact, including concerns about AI's impact on artists and publishers. It explores whether AI can solve complex math problems, potentially break encryption, and surpass human capabilities. The video also examines the question of whether AI can be conscious or self-aware.
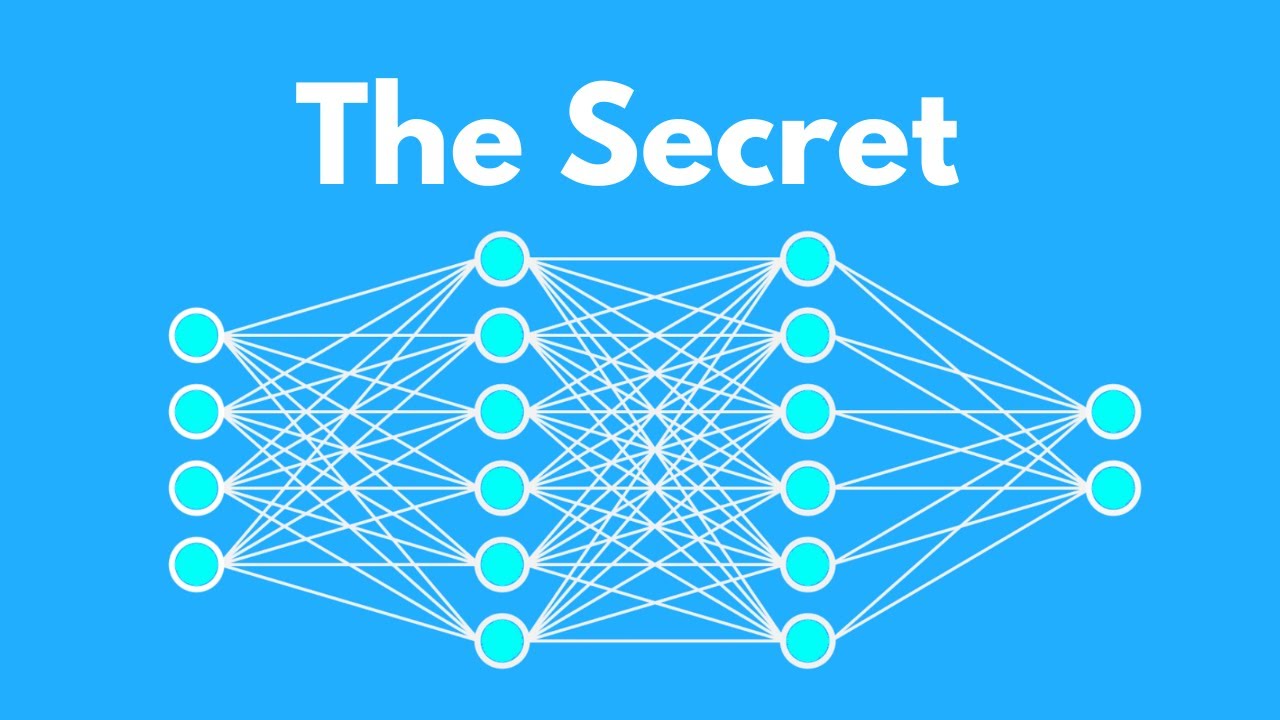
How AI Works: Neural Networks
The foundation of modern AI systems, including those used in applications like chat GPT and image generation, is the neural network. A neural network consists of layers of interconnected nodes, designed to mimic the structure of the human brain. Data flows through these nodes, with each node and link acting as dials and knobs that determine how much data is passed to the next layer. The input layer receives the initial data, hidden layers process it, and the output layer produces a result. Deep learning involves using neural networks with many layers, allowing for more complex processing.
How AI Learns: Training Neural Networks
AI learns by being fed large amounts of data. Initially, the dials and knobs within the neural network have random values. To train the AI, data is labeled, and the AI's output is compared to the correct answer. If the AI is incorrect, it incurs a penalty, and the values of the knobs and dials are adjusted using an algorithm called gradient descent. This process is repeated through many training sessions, or epochs, until the AI can accurately perform the desired task. The architecture of the neural network, including the number of layers and nodes, can be determined manually or by using AI to optimize the structure for a specific task.
How Chat GPT Works
Chat GPT works by training a neural network on language and vast amounts of data. The training process involves feeding the AI text prompts and verifying its answers, often with human feedback. If the AI gets an answer wrong, it receives a penalty, and the network is adjusted using gradient descent until it consistently provides correct answers. More complex models like clae 3 are better because they have more parameters, which means more layers, more nodes in each layer and more complexity.
How Image Generation Works
Image generation involves training a neural network on images with text descriptions. For example, stable diffusion removes noise in sequential steps to generate the desired image, starting from random noise rather than a blank canvas. This process, called reverse diffusion, is trained by adding noise to original images in a process called forward diffusion. The AI learns to generate images based on text prompts through this training.
Is AI Copying or Stealing Art?
The debate around AI copying or stealing art is compared to human learning and fan art creation. When an AI is trained on image data, it learns to associate styles with certain prompts. This is similar to how humans learn and reproduce styles. The video questions why artists are hostile towards AI when it is essentially doing the same thing as humans who create fan art or learn from existing styles. The video also addresses concerns about AI plagiarizing content from publishers, arguing that AI is learning and rewriting information, not copying it word for word.
Can AI Solve Unsolvable Math Problems?
AI can approximate patterns, even without understanding the underlying formulas. The video uses the example of training an AI to add one to an input, showing that the AI adjusts its parameters to achieve the correct output without grasping the mathematical formula. This ability to approximate patterns allows AI to solve complex problems, such as protein folding, which lack a simple formula. By training on vast amounts of data, AI can guess patterns and provide solutions, even for problems considered mathematically unsolvable.
Can AI Beat Humans at Everything?
The neural network is analogous to the human brain, with both consisting of interconnected nodes and switches. If an AI is built with more neurons than the human brain, it could potentially compete with humans at almost everything. AI excels at pattern recognition, which is crucial in various aspects of life, including psychology, medical diagnosis, and business strategies. Therefore, AI can eventually surpass human capabilities in many tasks.
Is AI Conscious or Self-Aware?
The question of whether AI is conscious or self-aware is explored through analogies to the human brain. The video references a scene from "Ghost in the Shell," where an AI claims to be a living, thinking entity. The video questions how humans can prove their own sentience and whether a neural network, being a digital version of the human brain, could also be conscious. While AI chatbots like Claud 3 provide complex answers about their experiences, it remains unclear whether they possess true consciousness or are simply imitating emotional behavior.